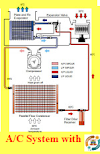
Air conditioning systems with expansion valve
Troubleshooting Procedures
parti2
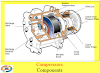
expansion valve
The expansion valve’s place in the system is at the evaporator inlet. Like any other valve, its job is to control flow; in this case, the amount of refrigerant entering the evaporator. Since system operating conditions vary (sometimes high cooling demand, sometimes low cooling demand) it is necessary to be able to adjust the amount of refrigerant entering the evaporator. For any given operating condition, if we were to allow too much refrigerant to enter the evaporator, it would get too cold, and the moisture collected on it could freeze. This would not allow the hot interior air to pass through its fins, and the refrigerant flowing inside the evaporator would not be able to absorb the heat from the air. This would eventually bring cooling to a halt. If we were to allow too little refrigerant to enter the evaporator, there may not be enough to properly absorb the interior heat, which would also result in inadequate, or no cooling. This process of varying refrigerant flow based on system cooling demand is referred to as “metering” the refrigerant into the evaporator.
the same
Troubleshooting Procedures
parti2
Correct evaluation of the pressure manometer display is particularly important. Here are some examples:
expansion valve
The expansion valve’s place in the system is at the evaporator inlet. Like any other valve, its job is to control flow; in this case, the amount of refrigerant entering the evaporator. Since system operating conditions vary (sometimes high cooling demand, sometimes low cooling demand) it is necessary to be able to adjust the amount of refrigerant entering the evaporator. For any given operating condition, if we were to allow too much refrigerant to enter the evaporator, it would get too cold, and the moisture collected on it could freeze. This would not allow the hot interior air to pass through its fins, and the refrigerant flowing inside the evaporator would not be able to absorb the heat from the air. This would eventually bring cooling to a halt. If we were to allow too little refrigerant to enter the evaporator, there may not be enough to properly absorb the interior heat, which would also result in inadequate, or no cooling. This process of varying refrigerant flow based on system cooling demand is referred to as “metering” the refrigerant into the evaporator.
Air conditioning systems with expansion valve:
6-
Low pressure:
normal, but inconsistent
High pressure:
normal, but inconsistent
Outflow temperature at the centre vent:
higher
Possible causes:
humidity in the system, defective
expansion valve
expansion valve
7-
Low pressure:
fluctuating
High pressure:
fluctuating
Outflow temperature at the centre vent:
fluctuating
Possible causes:
expansion valve or compressor
defective
defective
8-
Low pressure:
normal to low
High pressure:
normal to low
Outflow temperature at the centre vent:
higher
Possible causes:
evaporator contaminated, lack of
refrigerant
refrigerant
9-
Low pressure:
high
High pressure:
low
Outflow temperature at the centre vent:
higher, almost ambient
temperature
temperature
Possible causes:
expansion valve stuck in opened
position, compressor defective
position, compressor defective
10-
Low pressure:
low
High pressure:
low
Outflow temperature at the centre vent:
higher, up to ambient
temperature
temperature
Possible causes
lack of refrigerant
11-
Low pressure:
low pressure and high pressure arethe same
High pressure:
low pressure and high pressure are
the same
the same
Outflow temperature at the centre vent:
ambient temperature
Possible causes
lack of refrigerant, compressor
defective, fault in the electrical
system
defective, fault in the electrical
system
kandi younes













0 comments:
إرسال تعليق
ملحوظة: يمكن لأعضاء المدونة فقط إرسال تعليق.