Automotive
Air Conditioning
Air Conditioning
Pressure & temperature relationship
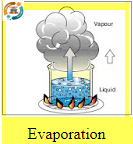
Evaporation:
Is the term used when enough heat is added to a liquid substance to change it into a vapor (gas). For example, when water is boiled.This condition occurs within the A/Csystem.
Condensation:
Is the term used to describe the opposite of the evaporation process. If you take a vapor and remove enough heat from it, a change of state occurs.The vapor becomes a liquid. The change of vapor to a liquid is called condensation. This condition occurs within the A/C system.
Freezing:
Is another change of state. Freezing results when heat is removed from a liquid substance until it becomes a solid. Remember that anything above -273 C still contains some heat. In an air conditioning system freezing must be avoided. Otherwise component damage will occur.
Pressure & temperature relationship:
To increase or decrease the boiling point of a substance, we must alter the pressure on
the substance. Increasing the pressure increases the boiling point.To decrease the boiling point, decrease the pressure.
the substance. Increasing the pressure increases the boiling point.To decrease the boiling point, decrease the pressure.
A good example is the automotive cooling system. The pressure cap keeps the radiator from
boiling over by increasing the pressure on the coolant.
Example:
110 kPa radiator cap allows the coolant temperature to reach 126 C before boiling.
This chart opposite shows that the boiling point of water can be altered by changing the pressure upon it. As a comparison with the radiator example above. The substance used in the air conditioning system, called refrigerant, also boils at different temperatures depending on the pressure that it is under.
kandi younes